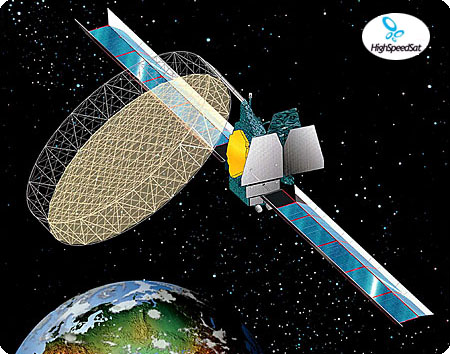
Thuraya Satellites
Two Thuraya Satellites were and third one is being built by Boeing Satellite Systems. The satellites are designed for a 12-15 year life. The satellite is equipped with an innovative 40-foot (12.25-meter) L-band transmit-receive reflector provided by TRW Astro Aerospace. The large reflector is combined with Boeing’s on-board digital signal processing to create an active phased-array antenna that allows the spacecraft to create more than 200 spot beams and handle 13,750 simultaneous phone calls. The digital signal processor, five times more capable than any previous Boeing digital processor, has more computing power than 3,000 Pentium III-based computers.
The Thuraya mobile communications system serves a region of 2.3 billion people. Boeing Satellite Systems (BSS) built the complete turnkey system under a contract signed on Sept. 11, 1997. This included the manufacture and October 2000 launch of Thuraya-1, a high-power Boeing GEM satellite, plus a second spacecraft, ground facilities and user handsets. The system began commercial operations in mid-2001. Sea Launch successfully orbited Thuraya-2 on June 10, 2003, and Thuraya-3 on January 15, 2008.
Thuraya 1 (HS-GEM)
Thuraya-1 is the first satellite in the Boeing GEM (Geomobile) series. This product line expands Boeing's offerings beyond satellite manufacturing, to integrate a high-power geosynchronous satellite (derived from the Boeing BSS_702 body-stabilized design) with a ground segment and user handsets, to provide a range of cellular-like voice and data services over a large geographic region. The Thuraya ground segment includes terrestrial gateways plus a collocated network operations center and satellite control facility in the UAE. Thuraya offers GSM-compatible mobile telephone services, transmitting and receiving calls through a single 12.25-meter-aperture reflector. The satellite employs state-of-the-art on-board digital signal processing to create more than 200 spot beams that can be redirected on-orbit, allowing the Thuraya system to adapt to business demands in real time. Calls are routed directly from one handheld unit to another, or to a terrestrial network. The system has the capacity for 13,750 simultaneous voice circuits. Thuraya 1 suffers from a generic failure of the early BSS-702 / GEM model: the fogging of the concentrator mirrors on the solar arrays leads to reduced available power.
Thuraya 2 and 3 (BSS-GEM)
Thuraya-2 and 3 are among the first satellites in the Boeing GEM (Geomobile) series. This product line expands Boeing's offerings beyond satellite manufacturing, to integrate a high-power geosynchronous satellite (derived from the Boeing BSS-702 body-stabilized design) with a ground segment and user handsets, to provide a range of cellular-like voice and data services over a large geographic region. The Thuraya ground segment includes terrestrial gateways plus a collocated network operations center and satellite control facility in the UAE. Thuraya offers GSM-compatible mobile telephone services, transmitting and receiving calls through a single 12.25 meter-aperture reflector. The satellite employs state-of-the-art on-board digital signal processing to create more than 200 spot beams that can be redirected on-orbit, allowing the Thuraya system to adapt to business demands in real time. Calls are routed directly from one handheld unit to another, or to a terrestrial network. The system has the capacity for 13,750 simultaneous voice circuits. Thuraya 2 and 3 have redesigned solar arrays, as the original concentrator arrays have a fogging problem reducing the performance.
Thuraya satellite communications provide satellite phone services mainly in the Middle East, Africa and Europe but are planning to extend its coverage to East Asia, Australia and South America. It is one of the principal rivals of Iridium Satellite LLC which provides global coverage. Thuraya is based in the United Arab Emirates. Thuraya satellite communications provide basic phone services, short message service (SMS), internet and data transfer services and Global Positioning System (GPS) services which help to find the precise location, speed, time and direction of a body (or rather a GPS receiver) anywhere on earth. Thuraya satellite communications use handsets made by Thuraya, Hughes and Ascom. Most Thuraya handsets have a dual-mode feature which allows them to operate in the Thuraya satellite network as well as in GSM terrestrial mobile networks. Thuraya has roaming agreements with more than 200 wireless cellular operators worldwide, allowing its customers the ability to use their Thuraya phones outside the Thuraya satellite coverage. The dual-mode feature of the Thuraya handsets is similar to the Qualcomm (CDMA/Satellite) and Telit (GSM/Satellite) handsets in the Globalstar system. Thuraya uses the virtual country calling code +882 16 which is part of the ITU-T International Networks numbering group. Thuraya is not a part of the +881 country calling code numbering group for this is allocated by ITU-T only for networks in the Global Mobile Satellite System and Thuraya is not a part of it as it is a regional instead of a global system. Thuraya operates two communications satellites (or comsats as they are also known as) in its system (or satellite constellation) which are built by Boeing. They also have a third communications satellite in orbit but it is not yet operational. Satellite phones work on the principle of global connectivity even on water or in an aeroplane as instead of submarine communication cables it uses satellite communication. Like all satellite communications system, Thuraya terminals need a relatively clear line of sight to the sky for connectivity. There may be problems in deeply forested areas or in mines. Satellite phones are primarily used by world travellers, scientists, marine officials and frequent fliers. With not too many satellite phone service providers, Thuraya satellite communications does not have too much competition yet it provides an alternative to the Iridium satellite system and its system of 66 low earth orbit (LEO) satellites. One of the other major competitors in the field of satellite communication service providers is Globalstar. Satellite communications though extremely useful for those working in remote places or frequent fliers, remains quite an expensive (though not extremely prohibitive) form of telecommunication. Thuraya satellite communications provide a cheaper alternative to Iridium in the places which are covered by Thuraya. Thuraya satellite communications are an important step in the field of satellite communications and with its plans to extend its services to more parts of the world, it is all set to add the diverse forms of telecommunication available to us today. This is a brief overview of Thuraya satellite communications.